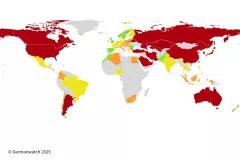
The Paris climate agreement aims at holding global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius and to “pursue efforts” to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius. To accomplish this, countries have submitted Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) outlining their post-2020 climate action. Here we assess the effect of current INDCs on reducing aggregate greenhouse gas emissions, its implications for achieving the temperature objective of the Paris climate agreement, and potential options for overachievement. The INDCs collectively lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to where current policies stand, but still imply a median warming of 2.6–3.1 degrees Celsius by 2100. More can be achieved, because the agreement stipulates that targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions are strengthened over time, both in ambition and scope. Substantial enhancement or over-delivery on current INDCs by additional national, sub-national and non-state actions is required to maintain a reasonable chance of meeting the target of keeping warming well below 2 degrees Celsius.
Full citation: Rogelj, J., den Elzen, M., Höhne, N., Fransen, T., Fekete, H., Winkler, H., Schaeffer, R., Sha, F., Riahi, K., Meinshausen, M. (2016). Paris Agreement climate proposals need a boost to keep warming well below 2°C. Nature, http://www.doi.org/10.1038/nature18307.